Nausea after Eating
Not medical advice.
Nausea after eating can have many potential causes, and if you’re suspecting an ulcer, that’s one of the more common gastrointestinal reasons. Here’s a breakdown of likely causes, starting with ulcers:
Most Likely Causes of Nausea After Eating
1. Peptic Ulcer (Stomach or Duodenal)
- Description: Open sore in the lining of the stomach (gastric ulcer) or upper small intestine (duodenal ulcer).
- Symptoms:
- Nausea, especially after meals
- Burning or gnawing pain in the upper abdomen
- Bloating
- Early satiety (feeling full quickly)
- Pain may improve or worsen with food (depends on ulcer location)
- Causes:
- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection
- Long-term NSAID use (ibuprofen, aspirin)
- Stress, smoking, alcohol
2. Gastritis
- Description: Inflammation of the stomach lining, often co-occurs with ulcers.
- Symptoms: Nausea, pain after eating, indigestion, appetite loss
- Causes: H. pylori, NSAIDs, alcohol, stress
3. Gallbladder Disease (e.g., Gallstones, Cholecystitis)
- Symptoms: Nausea after fatty meals, upper right abdominal pain, bloating
- Risk: Worse after heavy or greasy meals
4. GERD (Acid Reflux)
- Symptoms: Nausea, heartburn, regurgitation, worse when lying down
- Cause: Weak esophageal sphincter allows acid into the esophagus
5. Delayed Gastric Emptying (Gastroparesis)
- Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting undigested food, fullness after small meals
- Common in: Diabetics, people with vagus nerve damage
6. Food Intolerances / Sensitivities
- Examples: Lactose intolerance, gluten sensitivity
- Symptoms: Nausea, bloating, cramping, diarrhea after specific foods
Less Common but Possible Causes
- Pancreatitis
- Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
- Functional dyspepsia (non-ulcer indigestion)
- Anxiety or stress-related nausea
- Medication side effects
What to Do Next
- Test for H. pylori: Breath, stool, or blood test
- Endoscopy: To confirm presence of ulcers or gastritis
- Ultrasound: For gallbladder check
- Elimination diet: To rule out food-related causes
Here are natural treatments for nausea after eating, especially when related to ulcers, gastritis, or mild digestive dysfunction:
Natural Treatments for Nausea After Eating (Ulcer-Focused)
1. Slippery Elm
- What it does: Coats the stomach lining and reduces irritation.
- How to use: Mix 1 tsp of slippery elm powder in warm water after meals.
- Best for: Ulcers, gastritis, acid reflux.
2. Deglycyrrhizinated Licorice (DGL)
- What it does: Soothes the stomach lining, reduces acid, promotes healing.
- How to use: Chewable tablets 20 minutes before meals.
- Avoid: If you have high blood pressure unless it’s the deglycyrrhizinated form.
3. Aloe Vera Juice (Inner Leaf Only)
- What it does: Anti-inflammatory, soothes mucosal tissues.
- How to use: 1/4 cup on an empty stomach, twice daily.
- Note: Must be food-grade and free of latex (the outer leaf component which can irritate bowels).
4. Ginger Root
- What it does: Classic anti-nausea remedy, helps with motility.
- How to use: Ginger tea (fresh slices steeped 10+ min), or 500mg capsule 1–2x/day.
5. Chamomile Tea
- What it does: Calms nerves and the digestive tract.
- Best for: Stress-related gastritis or nausea, helps sleep too.
6. Marshmallow Root
- What it does: Similar to slippery elm; coats and protects the stomach lining.
- How to use: Cold infusion (soak overnight) or capsules.
7. Manuka Honey (UMF 10+ or higher)
- What it does: Natural antibacterial (especially helpful for H. pylori), wound-healing.
- How to use: 1 tsp on an empty stomach in the morning and before bed.
Foods to Avoid
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
- NSAIDs (aspirin, ibuprofen)
- Fried/fatty foods
- Spicy foods
- Carbonated beverages
Supportive Lifestyle Measures
- Eat small, frequent meals
- Elevate head while sleeping (if reflux is present)
- Don’t lie down right after eating
- Quit smoking (if applicable)
- Stress management: yoga, walking, meditation
Here is a detailed natural protocol for eradicating Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), the primary cause of ulcers, chronic gastritis, and often nausea after eating — without antibiotics:
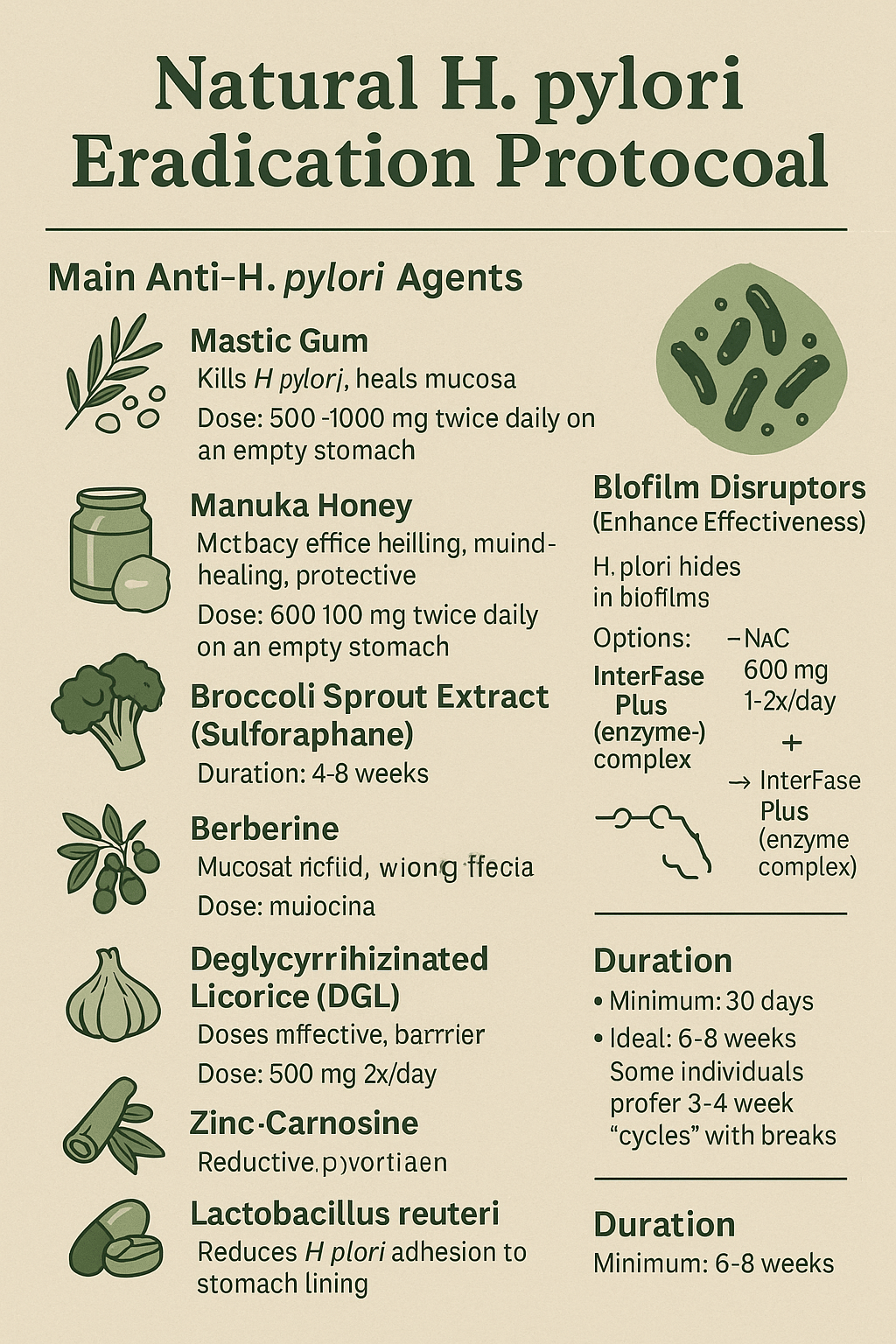
Natural H. pylori Eradication Protocol
Main Anti-H. pylori Agents
1. Mastic Gum (Pistacia lentiscus)
- Action: Kills H. pylori, heals mucosa.
- Dose: 500–1000 mg twice daily on an empty stomach.
- Duration: 4–8 weeks minimum.
- Study-backed: Proven effective in reducing H. pylori populations.
2. Manuka Honey (UMF 10+ or higher)
- Action: Antibacterial, wound healing.
- Dose: 1 tsp 2–3x/day on empty stomach.
- Tip: Take first thing in morning and before bed.
3. Broccoli Sprout Extract (Sulforaphane)
- Action: Detoxifier, potent H. pylori suppressant.
- Forms: Capsules, powders, or fresh sprouts.
- Dose: 1–2 tsp/day of powder, or 60–120 mg sulforaphane.
- Duration: 4–6 weeks.
- Study: Sulforaphane shown to suppress H. pylori and protect gastric lining.
4. Berberine
- Action: Antimicrobial, especially effective on GI pathogens.
- Dose: 500 mg 2–3x/day with meals.
- Sources: Goldenseal, Oregon grape root, barberry.
5. Deglycyrrhizinated Licorice (DGL)
- Action: Mucosal healing, protective barrier.
- Dose: 380 mg chewable 20 minutes before meals.
- Duration: 4–6 weeks.
- Important: Use DGL form to avoid blood pressure issues.
Biofilm Disruptors (Enhance Effectiveness)
H. pylori hides in biofilms, making it hard to eradicate.
Options:
- N-acetylcysteine (NAC): 600 mg 1–2x/day
- InterFase Plus (a professional-grade enzyme complex)
These can be taken 30–60 minutes before antimicrobials to weaken biofilm defenses.
Optional Additions
- Propolis Extract: Natural antibiotic. 500 mg 2x/day.
- Garlic (allicin extract): 600–1200 mg/day standardized allicin.
- Zinc-Carnosine: Helps heal stomach lining. 75 mg 2x/day.
- Lactobacillus reuteri: A probiotic shown to reduce H. pylori adhesion to stomach lining.
Sample Daily Protocol
| Time | Supplement |
|---|---|
| AM (fasted) | Mastic Gum + Manuka Honey + NAC |
| Breakfast | Berberine + Sulforaphane + Probiotic |
| Lunch | Berberine + Sulforaphane + Zinc-Carnosine |
| 20 min pre-dinner | DGL chewable |
| Dinner | Berberine + Sulforaphane + Probiotic |
| Bedtime | Mastic Gum + Manuka Honey + NAC |
Duration
- Minimum: 30 days
- Ideal: 6–8 weeks
- Some do 3–4 week “cycles” with breaks.
Diet Recommendations
- Avoid sugar, dairy, alcohol, refined carbs
- Emphasize:
- Cabbage juice (raw, ½ cup daily)
- Bone broth
- Wild blueberries
- Garlic, ginger, turmeric
- Fermented foods (unless sensitive)