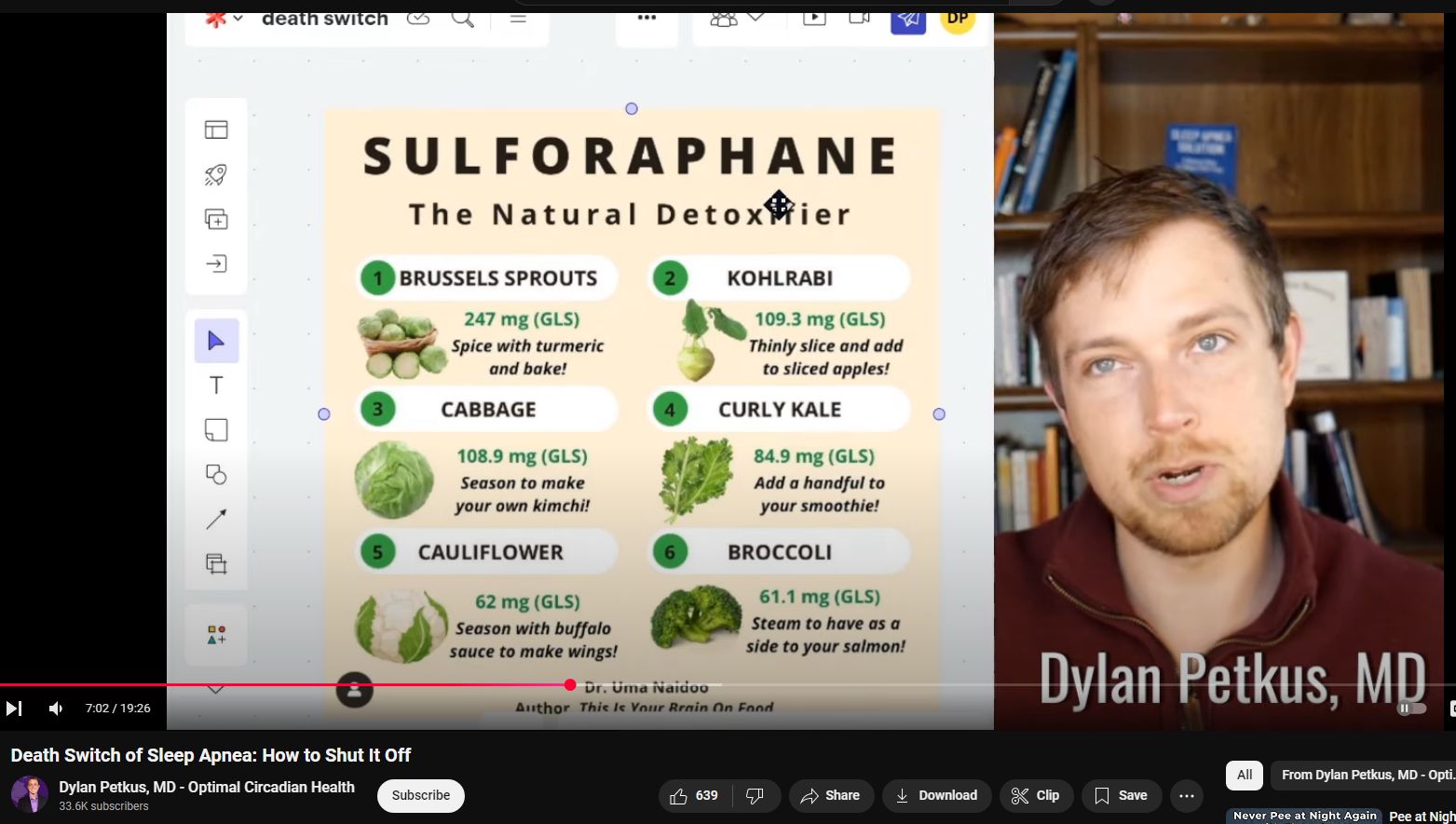
END SLEEP APNEA with a bedtime vegetable nibble — SULFORAPHANE from cruciferous vegetables reduces HIF1a protein trigger for Sleep Apnea
Kudos. Dr Dylan is quite thorough and sensible.
MIT’s Prof Stephanie Seneff has for many years railed about the many negative effects caused by the citizenry’s perilously low sulfur intake. That a sulfur compound is an answer is unsurprising given her research. Great cross-tie; I don’t remember hearing her ever mention sleep apnea as a consequence of low sulfur. 4 WELLNESS ORGanization has more.
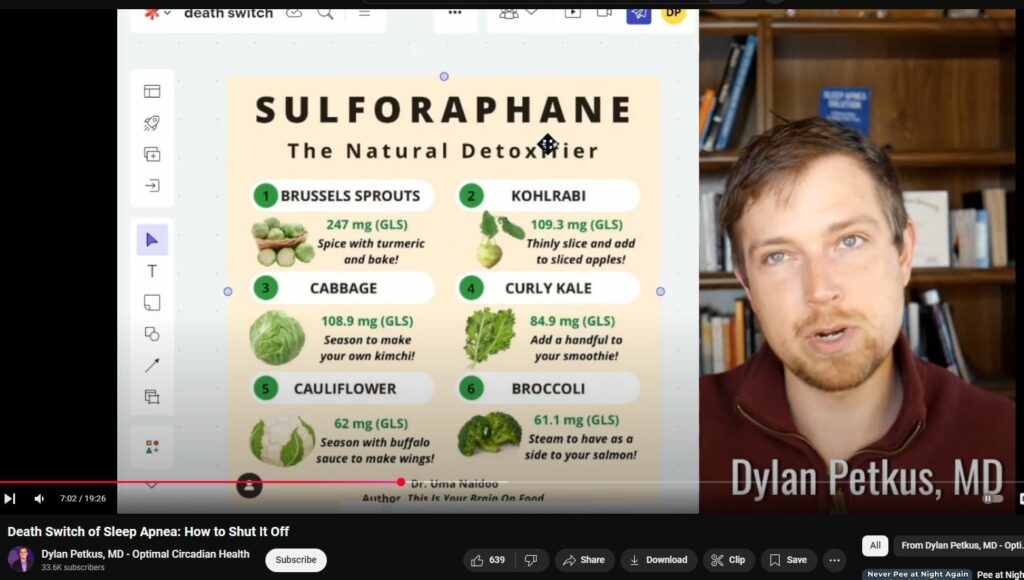
Yes, broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts are all cruciferous vegetables.
“Cruciferous” refers to plants in the family Brassicaceae (formerly Cruciferae), which comes from the Latin word crucifer, meaning “cross-bearing.” This name was chosen because their flowers typically have four petals arranged in the shape of a cross.
Common Cruciferous Vegetables:
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
- Cabbage
- Brussels sprouts
- Kale
- Bok choy
- Arugula
- Turnips
- Radishes
Nutritional Benefits:
Cruciferous vegetables are highly nutritious and contain beneficial compounds such as:
- Fiber: Supports digestive health.
- Vitamin C and K: Important for immune support and bone health.
- Glucosinolates: Compounds that are broken down into biologically active substances like sulforaphane and indole-3-carbinol, which have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and potential anti-cancer properties.
Eating a variety of these vegetables regularly is linked to reduced risks of chronic diseases, including certain types of cancers, heart disease, and inflammation.
Broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts are cruciferous vegetables that contain sulforaphane, a compound known for its potential health benefits. Research indicates that sulforaphane may influence pathways related to hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α), which is implicated in conditions like obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Understanding HIF-1α and Sleep Apnea:
OSA is characterized by repeated episodes of partial or complete obstruction of the upper airway during sleep, leading to intermittent hypoxia (IH)—fluctuating oxygen levels in the body. This IH condition can activate HIF-1α, a transcription factor that responds to low oxygen levels by regulating genes involved in adaptation to hypoxia. Chronic activation of HIF-1α due to IH is associated with various pathological processes, including inflammation, oxidative stress, and metabolic dysfunction, all of which can exacerbate OSA and its related complications.
Sulforaphane’s Role:
Sulforaphane has been studied for its potential to modulate the effects of IH:
- Neuroprotection: In a mouse model simulating OSA, sulforaphane administration attenuated cognitive impairments induced by IH. The compound enhanced nuclear translocation of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), leading to increased antioxidant defenses and reduced neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampus.
- Cardioprotection: Sulforaphane demonstrated protective effects against IH-induced cardiomyopathy in mice. This protection was associated with the activation of Nrf2 pathways, suggesting a mitigation of oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiac tissues.
Conclusion:
While sulforaphane shows promise in mitigating some adverse effects of IH—such as oxidative stress and inflammation—direct evidence linking sulforaphane intake to reduced HIF-1α activity and subsequent improvement in sleep apnea severity is limited. Most studies have been conducted in animal models, and more research, particularly clinical trials in humans, is necessary to establish sulforaphane’s efficacy in this context. Nonetheless, incorporating cruciferous vegetables rich in sulforaphane into one’s diet may offer general health benefits and could potentially support the management of conditions associated with oxidative stress and inflammation.
Here are the text-only hyperlinks supporting the connection between cruciferous vegetables, sulforaphane, HIF-1α, and sleep apnea:
These sources detail the role of sulforaphane in modulating pathways associated with intermittent hypoxia, oxidative stress, and inflammation, which are implicated in sleep apnea through HIF-1α signaling.
Transcript
sleep apnea has something known as a
0:02
death switch and know it's not from
0:03
Austin Powers or Dr Evil but it is
0:06
inside of your cells and it can make the
0:08
difference between whether the apne
0:10
episodes you're soring at night is
0:12
massively damaging to your cells and
0:14
your entire body or if you learn how to
0:16
turn it off because you watch this
0:18
episode it can actually reduce the
0:20
damage that you're accumulating at night
0:22
so you actually have way better sleep
0:24
and you're not having as many of the
0:26
adverse side effects of having sleep
0:28
apnea and by side effects we're talking
0:31
about like things that are damaging your
0:32
heart or your brain so this death switch
0:35
is a little important so this is like a
0:38
bunch of dominoes because we know with
0:39
sleep apnea the big issue or so we think
0:43
the big issue is the change in oxygen it
0:46
goes up it goes down it leavs the damage
0:48
in our body and then as a result all
0:51
these bad things happen throughout like
0:54
I said heart arteries Etc but there's
0:57
this little thing in the middle that's
0:59
actually what mediates or allows the
1:01
damage from oxygen swings to happen and
1:04
this domino effect if you're able to
1:07
stop that one Domino then you also stop
1:10
the damage inside of the cells and can
1:12
put out the fires this is huge news
1:15
because this is something that can be
1:16
done before you fully fix the problem
1:19
with breathing at night now obviously
1:21
you still want to do that but this is a
1:22
good stop Gap measure to improve your
1:25
overall health so I want to talk about
1:27
what this death switch is more in depth
1:29
and how to flip it off and of course
1:32
this is for educational purposes only
1:34
always talk to your doctor before
1:36
changing anything with your health
1:38
regimen and of course you don't need to
1:40
talk to your doctor about subscribing to
1:41
this channel you can just go ahead and
1:43
do that that's personal advice for me to
1:46
you so what is this death switch here
1:49
and that's funny the exact same
1:51
diagram just copy and paste it and it's
1:55
known as
1:56
hi1 that is the name of this protein it
1:59
stands for hypoxia inducible Factor one
2:01
alpha yes the one alpha is important
2:05
keep that in a few neurons in the back
2:06
of your mind and this is what's going to
2:09
mediate the damage from hypoxia so as
2:12
the name would imply when you have
2:14
hypoxia then you activate hypoxia
2:17
inducible
2:19
Factor they they name things relatively
2:22
well here well sometimes in science here
2:25
and when they look at this protein in
2:27
people with sleep apneia it is way way
2:31
higher about twice as high here so on
2:33
the left this is people with obstructive
2:35
sleep apnea on the right are normal
2:38
people people say bapa nearly twice as
2:41
high like 1500 compared to like 700 way
2:44
higher and that's a big part of what
2:46
causes the damage throughout all the
2:48
cells here so if we just go through a
2:49
few here and this hif this is what
2:52
causes a lot of the damage inside the
2:54
cells so let's think of some common
2:56
problems whle bapy we can talk about
2:58
diabetes weight game okay well that's
3:01
going to be rooted in insulin
3:03
dysfunction well what's causing damage
3:05
to the cells that make insulin in your
3:07
body oh there it is hi that's what's
3:11
causing this Downstream Cascade of
3:13
problems inside of our pancreatic beta
3:15
cells what about brain fog dementia
3:18
things like that oh look at that hif
3:21
once again is causing all these issues
3:23
Downstream again you can see how this is
3:25
a domino yes hypoxia can come in oxygen
3:28
can become a problem
3:30
and then that induces this and causes
3:32
damage so this is the Domino here so
3:34
that's what we want to really focus in
3:36
on and also thought this was interesting
3:39
as well this is the main thing that's
3:41
going to mediate the damage and increase
3:43
in cancer in sleep bin that's the I
3:46
always talk about with sleep abin but
3:48
this is one of the main ways in which
3:50
that goes way way higher so this is what
3:54
we want to really focus it on and then
3:56
here's another diagram in case this
3:57
horse is still alive
4:00
hopefully you kind of get that joke is
4:02
that these are arteries and once again
4:05
hif is going to activate there once
4:07
again L oxygen all these dominoes but
4:10
hif it's kind of the last like you know
4:13
what was that like in Lord of the Rings
4:14
when they're in that last place and it's
4:16
the the last like
4:18
Fortress it's like that someone correct
4:20
me in the comments of what that is and
4:22
of course just to make sure we're not
4:24
just making stuff up with science
4:25
because that's not great we should ask
4:28
ourselves well if you could just turn
4:29
turn off hif-1 what would that do to a
4:32
lot of these different processes luckily
4:34
people with some rats were just hanging
4:36
around and decided to do this with some
4:38
transgenic rats here and what they found
4:41
is that when you selectively block hi
4:46
with this compound here you know
4:48
everyone's favorite Acro flaven which is
4:51
not good for human consumption any way
4:53
shape or form so don't do that when you
4:56
use this that will actually reduce the
4:59
impact of intermittent hypoxia
5:02
IH so blackly it is there the the proof
5:07
of concept around that now we just need
5:09
to talk about how we flip it off so
5:12
that's what we're going to do next here
5:15
okay and I hope you're enjoying my
5:17
slightly zoomed out approach someone
5:19
told me my face was too big and I
5:21
figured uh you know give it a zoom out
5:23
maybe you can see my bookshelf and uh
5:25
enjoying oh look at that book there look
5:27
at that yeah you can
5:30
it's my book so an earlier Edition at
5:34
least so flipping the switch off here so
5:37
they did some studies and they were
5:39
looking at different compounds that
5:41
could turn off hif and I'm sure as you
5:43
know this is a western blot everybody's
5:45
favorite
5:46
thing if you don't know what a western
5:48
blot is that's fine you're like most
5:50
normal people who shouldn't know what
5:52
this is and you're having a normal
5:54
healthy existence but if you do I'm
5:57
sorry but all they do here is they look
5:59
at if we add in different compounds what
6:02
happens to the amount of hif in
6:05
different tissues and they like
6:06
homogenize it put in the blender and do
6:08
this so the darker it is that means
6:10
there's more Hi and then the lighter or
6:13
non-existent means there's less so when
6:15
you give more of this compound hif goes
6:18
way way down and even when you add
6:22
hypoxia into the mix so it blocks the
6:25
impact of it here just the hammer this
6:28
home they also look at the cells here
6:30
before they put them in a blender the
6:32
top is hypoxia but without this compound
6:36
so we have some red irritated cells
6:38
they're cranky and then on the bottom we
6:41
have hypoxia still but then we added in
6:43
a little bit of this compound and cells
6:46
are are pretty much normal here so
6:49
that's good that's what we would want so
6:51
what is this compound so this compound
6:54
is
6:54
sophene which is containing all these
6:57
lovely foods and I'll never understand
6:59
why
7:00
when they want something to be really
7:01
obvious to read they'll put it in all
7:03
caps and do this weird spacing I've
7:05
never understood that like why would
7:06
they make all caps anyway so having more
7:09
self furanes in your diet will help
7:11
achieve that effect and there's many
7:13
other ways to modulate hif this is just
7:15
one so brussels sprouts are going to be
7:17
important col Robie which is kind of
7:18
gross so just go on down the Cabbage
7:20
kale things of that nature those are
7:22
going to contain certain amounts as
7:24
shown here of that sulfurane compound
7:28
here so if you're going for maybe like
7:31
200 300 milligrams of GLS we won't even
7:33
get into that that would be a amount
7:36
that's been shown to have that effect on
7:39
hi so about just brussels sprouts every
7:43
single day if you go higher that's
7:45
fine you can just enjoy brussels sprouts
7:48
and cabbage even more now the next best
7:51
thing and I'm trying to remember what
7:54
mental state I was in when I just copy
7:55
and pasted this one I don't know soone
7:59
name movie the next best thing for selfo
8:01
f is to subscribe because I know I talk
8:04
a lot about many different ways to
8:06
approach the bapa and it's not about
8:08
having any one thing be helpful as
8:11
Sensational and excited as I can get
8:13
about things it's about having as many
8:14
Tools in your toolkit as you can when
8:17
you're out there by yourself doing your
8:18
thing so to continue to grab those tools
8:21
and have success make sure you subscribe
8:23
because when you do YouTube will let you
8:25
know hey this guy's making videos here's
8:27
some more videos by him and will also
8:30
send a signal to like hey there's other
8:31
people who may want to see videos like
8:33
this so please go ahead and click
8:36
subscribe and then the next thing you
8:37
can do is Click some flavonoids so what
8:41
the heck is this let me kind of zoom in
8:44
here on this somewhat fuzzy diagram so
8:48
here's a cell and inside here zooming
8:51
way in this is
8:53
hif1 Alpha and again that'll be
8:56
important to know Alpha versus something
8:58
else in a moment
9:00
and you can modulate it in many ways so
9:02
fanes are just one and a lot of these
9:06
flavonoids are other compounds so quim
9:11
egcg and many of these other things I
9:13
know
9:15
uh well I thought that was going to be
9:16
Lin but it's
9:18
lolan so meaning these top two compounds
9:20
are more approachable in terms of
9:22
getting these whether it's purple onions
9:25
Capers First's also available in a
9:27
supplement form same thing for egcg and
9:30
that's why those two compounds are also
9:32
very well known for being anti-cancer in
9:35
a way because hif and cancer kind of go
9:38
hand in hand it's kind of a little bit
9:40
of a different pathway there's some more
9:42
steps involved but it's still a wi slate
9:44
babum will lead to higher rates of
9:45
cancer because hif gets activated way
9:48
too many times but those flavonoids
9:51
especially Quin egcg are helpful in
9:54
turning that off so egcg whether was
9:58
that like ban B the bgs or I'm thinking
10:00
of something else acbg
10:03
club I'm not sure but I'll keep that
10:05
rambling in the video for someone to
10:08
comment on green tea is how you can do
10:11
this and it's your choice really I mean
10:14
everything's your choice I would say I'm
10:15
not going to come over and Brew you
10:17
green tea oh that could sound relaxing
10:20
to an extent uh but you want to aim for
10:22
a certain amounts and usually around
10:24
like in studies people start to have a
10:27
positive effect around 500 Mig
10:30
so of egcg so that's why like the the
10:33
capsules will be around those or four
10:36
cups of green tea obviously that can
10:38
contain quite a bit amount of caffeine
10:41
that you want to look for I I guess like
10:43
9 milligrams isn't a whole lot that
10:46
might be decaf but always make sure to
10:49
balance that because sometimes people
10:51
get a little too strong out on caffeine
10:52
and you know not not super great so find
10:56
your best way you get some more egcg in
10:58
your day and the last thing is what I've
11:01
been hinting at a few times this whole
11:03
Alpha versus something else so sort of
11:07
premise this let's show the diagram yeah
11:09
let's go to the diagram first so I've
11:11
been talking about Alpha and dropping
11:13
some hints about this because Alpha is
11:16
always paired up with
11:18
beta and a gross simplification is that
11:23
they're like on a seesaw together in
11:26
case you ever wonder why it was Happ a
11:29
part of me on the screen so I can wave
11:32
my hands at you and Alpha if it's too
11:36
high in comparison to Beta then you'll
11:37
have bad things happen from hif but if
11:41
beta is higher than Alpha it'll be
11:45
actually good for you so it's about this
11:49
balance between these two and that's
11:50
what
11:51
allows for this phenomenon known as
11:55
adaptive hypoxia versus nonadaptive
11:58
hypoxia
11:59
the Adaptive hypoxia is when you have
12:03
the beta the beta is
12:06
dominating non-adaptive or bad hypoxia
12:09
would be alpha hif1 alpha is dominating
12:13
and depending on the expression let's
12:15
say we have non-adaptive this is all the
12:16
bad things we talked about inflammation
12:19
bad blood vessel growth that could allow
12:21
cancer to grow long-term activation more
12:25
oxidative stress whereas adaptive is it
12:29
will help increase cell resiliency by
12:31
keeping cells alive in low oxygen States
12:35
you think that might be something we
12:36
want May a little bit right and it can
12:40
help defend and reduce
12:43
inflammation so that's good that's what
12:46
we want and in case you're a smart
12:48
cooking you've realize it says increases
12:50
blood vessels for the good and the bad
12:52
not all blood vessel growth is the same
12:55
some can lead to better oxygen delivery
12:58
to smaller tissues that are starving
13:00
this one over here the bad one can lead
13:02
to changes in blood vessels that leads
13:04
to hypertension and like I said cancer
13:06
growth so very
13:09
dependent so how do we activate
13:12
different ones kind already said this
13:13
one so with working on the breathing
13:17
exercises and there's a lot of them but
13:20
they'll all help contribute to different
13:22
levels to this good adaptive hypoxia
13:27
because if you're doing say box
13:28
breathing
13:30
or if you increase the pause longer the
13:32
exhale longer you will find if you if
13:34
you had a pul Sox and you put it on your
13:36
finger your oxy levels will go down and
13:40
they'll come back up in a fashion that
13:42
is very similar to if you looked at
13:45
someone's oxygen levels at
13:47
night so when that happens we have to
13:51
ask ourselves
13:52
wait why is it bad at night but good
13:56
during the day aren't these like very
13:58
similar they are but they're very
14:01
different in intensity so think of it
14:03
like
14:05
this say you want to get in shape to run
14:07
a
14:08
marathon you could option a plan to run
14:12
a few miles every single day have rest
14:14
and Recovery Etc or option b you could
14:17
hire a lion to chase you in the middle
14:19
of the night when you should be resting
14:21
uh you'll get your miles in for sure but
14:24
at what cost so option A is obviously
14:27
the Adaptive hypoc option b is the
14:30
non-adaptive when your body is supposed
14:32
to be resting and you're adding a
14:33
structure on top of it it's going to
14:35
clash it's not going to mix it's going
14:37
to be bad long term if you do something
14:39
stressful to your body in a controlled
14:41
manner that allows for Recovery then
14:44
it's a good stress you benefit from that
14:46
stress that's what adaptive hypoxia is
14:49
all about now I've talked about this few
14:52
times not very often but when I'm
14:55
talking about typically improving the
14:57
relaxed pause that's more of a
14:59
conversation around CO2 carbon dioxide
15:02
whereas adaptive hypoxia if we really
15:04
want to Target that even more it will be
15:07
training oxygen and your tolerance to
15:11
hypoxia now talk to your doctor about
15:13
what is appropriate for you in breath
15:15
holding breath holding just because you
15:16
did it in a pool when you're eight years
15:18
old or maybe still uh doesn't mean it's
15:22
you know it can be a dangerous activity
15:23
never do it in
15:24
water all right so unless you have like
15:28
you supervisors and a lifeguard or
15:30
something like that but what that looks
15:32
like is say you just breathe normally
15:34
for like two minutes and then at the end
15:36
of that two minutes you do an
15:38
inhale and then you hold for a
15:41
minute and then breathe normally for two
15:44
minutes then after a big inhale hold for
15:48
minute 15 and this will help start to
15:50
train your body to low levels of ox in a
15:53
safe controlled manner now everybody
15:55
will vary in what is appropriate for
15:58
their body so I don't like push it okay
16:01
they was never advised doing that but
16:03
that's the general idea of how you can
16:05
activate the good hypoxia because then
16:07
at night your cells will be a lot more
16:11
resilient and I know that sounds like a
16:13
bunch of Hocus Pocus but when we see it
16:16
one of the first things we see in
16:18
working with someone will be looking at
16:19
their overnight um you know pul Haw and
16:25
as someone progresses with the breathing
16:26
exercises you'll start to see that there
16:28
their heart rate doesn't react like it
16:31
doesn't Spike when their oxygen levels
16:34
dip because usually they they go
16:37
together oxygen goes down heart rate
16:38
goes up that's a sign of your body not
16:41
being well adapted to low levels of
16:43
oxygen now if you are well adapted then
16:46
oxygen could go down but then your body
16:48
doesn't freak out this that freak out
16:50
that means those dominoes have already
16:52
fallen across and things aren't good but
16:54
if your body can tolerate hypox then
16:56
it's less damaging so that's to look for
17:00
you know for for those tracking at home
17:03
now for all that written out over here
17:07
you know me with my my three great
17:09
options got the switch and sleep apnea
17:12
guide so you can do all your lovely
17:15
breath holding and Russel Sprout eating
17:18
in peace and then we also have the Sleep
17:20
apne reset protocol that helps you
17:22
Target and look at more individualized
17:26
ways for you to apply breathing
17:27
exercises to yourself and also
17:29
strengthen Airway muscles so you can
17:31
have a Airway that is nice and strong
17:34
with a nice slow steady inhale and
17:36
everything is groovy and Ruby Tuesdays
17:39
from that not sure why I said Ruby
17:41
Tuesdays I think I've eaten there once
17:44
in my life Ness that's available for you
17:47
well the Sleep AP reset protocol not not
17:50
a hamburger at Ruby Tuesdays uh you can
17:53
click the screen for that and for both
17:55
of them and I know I said three things
17:58
we'll get to the third thing thing in a
17:59
moment for both of them you can find
18:01
them in the description box so if you uh
18:04
click the title on your phone at least
18:07
then that'll open that box up you'll
18:09
have links in there you press that and
18:11
then there should have been a link up on
18:14
the screen and there's also a link below
18:16
for the reset protocol there so that's
18:19
how that goes and if you like URLs and
18:22
stuff which I'm sure you do get the
18:25
switch guide go to ow.com
18:28
twitch and then for the reset guy go to
18:30
ow.com
18:33
SLR and there's some QR codes available
18:36
for you as well you just grab your phone
18:38
I don't know where mine is so I guess I
18:40
know what I'm doing after filming this
18:42
TR to find it but you would just scan
18:45
one of those press the button takes you
18:47
away to where you need to go and of
18:49
course you can also press the Subscribe
18:52
button and then option three I like to
18:55
put those in there I space and house I
18:57
don't forget because apparently it is
19:00
very helpful in having more people here
19:03
and of course you want to learn more
19:04
about working with us directly you can
19:06
go to ow.com
19:08
nextt and there is your QR code as well
19:14
so so thank you for watching if you want
19:17
to scan this I mean you can always
19:19
rewind all right um and go with whatever
19:22
option best suits you thanks for
19:25
watching and I'll see you soon